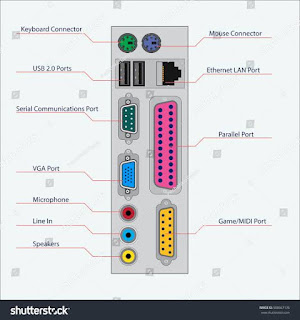
PORTS OF COMPUTER (CPU)
PORTS
Ø An
interface on a computer to which input/output Devices can be connected.
Physical ports allow
Ø
Types or ports:
o Physical
(hardware) ports: connecting cables to
computers, routers, modems and other peripheral devices like disk drives,
display screens, and keyboards. Externally,
personal computers have ports for connecting modems, printers, mice.
o Virtual
or logical ports: these ports allow software
applications to share hardware resources without interfering with each other.
Computer and routers automatically manage network traffic traveling via their
virtual ports. For example – port no 21, post no 25.
TYPE
OF PORTS:
Ø Ps/2
(personal system) ports (6 pins).
Ø Display
port (15 pins) / USB port.
Ø Com
ports/serial ports (9 pins).
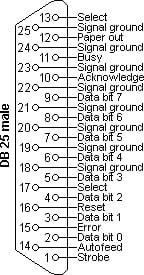
Ø Parallel
ports (LPT) (25 pins).
Ø USB
ports (4 pin).
Ø SCSI (50/68 pin).
Data
TRF rate 80 mbps (megabyte per second).
Ø IRDA
(infrared developers association) - optical.
Data
TFR rate 4 mbps.
Ø Bluetooth - radio.
Data
TRF rate 723 kbps (kilobyte per second).
PS 2
PORTS (6 PINS):
PORTS
VIEW:
COM/SERIAL PORTS (9 PINS):
WORKS
OF PARALLEL PORTS (25 PINS):
IRDA:
BLUETOOTH:
UNIVERSAL SERIAL BUS (4 PINS):
Ø USB
port was released on 1996.
Ø It was developed to replace the serial and parallel
ports.
Ø USB
ports data transfer rate is 12 mbps.
Ø A
single USB port can connect 127 peripheral. For eg. Mice, modems, and
keyboards.
Ø USB
is a plug-and-play installation device.
Ø USB
cables max length is 5 m.
Ø No
damage to a running computer while the USB.
4 PORT USB HUB:
SLOTS
SLOTS:
Ø
There are many
external devices which require to be connected with the motherboard.
Motherboard have socket to connect those devices. That socket is called slot.
TYPE
OF SLOTS:
Ø Expansion
slots.
ISA slots.
PCI slots.
AGP slot.
Ø IDE
slots.
Ø CPU
slot.
Ø RAM
slots.
WHAT
IS ISA:
Ø ISA
stands for industry standard architecture.
Ø It
controls the sound, video display
and other peripherals.
Ø ISA
is an older style that is typically found on computers with 286, 386 and
486 microprocessors.
Ø 8 bit version
of ISA supports clock peed
of 8 and 33 MHz and uses 64 pins connection.
Ø 16
bit version of ISA supports the same clock speed and uses 92 pins connection.
Ø Isa
slot may be used to
add a video
card, a network
card or an extra serial port.
Ø It was developed in 1981 and it remained the most common expansion
bus for most of the 1980s and 1990s
B But PCI and AGP replaced it by the end of twenty century.
ISA SLOT:
ISA CARD:
WHAT IS PCI? :Ø PCI
stands for peripheral component inter connect. It is found in most pcs from
late 486 models to the new Pentium 3.
Ø It
supports clock speed of 33 MHz - 66 MHz (Pentium) and a 32-bit data bus.
Ø The PCI
bus has a
special chipset which allows more sophisticated control over
the devices.
Ø PCI
is used for modem, sound card and LAN cards etc.
PCI
SLOT:
PCI CARD:
WHAT IS IDE? :Ø IDE
stands for integrated drive electronics and is found in most pcs.
Ø IDE
slots are used to connect hard disk drive, CD-ROM drive and floppy drive.
Ø There are normally 2
channels per IDE controller with a maximum of 2 ide devices per channel.
Ø Original
IDE standard could only support hard drives containing up to 540 MB of data.
Ø But
later it was replaced by EIDE (enhanced-ide), which supports hard drives with
over 250 GB of data. It also allows for data transfer rates that are over twice
as fast as the original IDE.
IDE SLOTS:
WHAT IS AGP? :Ø AGP
stands for accelerated graphics port.
Ø AGP
is based on the PCI standard, but is designed especially for the throughout
demands of 3-d graphics.
Ø The
AGP channel is 32 bits wide and runs at 66 MHz.
Ø AGP
version 1.0, 2.0 and 3.0 which each uses a different voltage. Therefore, AGP
cards must be compatible with the specification of the AGP slot they are
installed in.
Ø Later
it was also replaced by PCI express after 2006.
AGP SLOT:
Ø
One PCI express x16 connector supporting simultaneous transfer speeds up to 8 GBYTES/
sec.
Ø
One
PCI express x1 connector. The x1
interface supports simultaneous transfer speeds up to 500 MBBYTES/sec.
Ø
The
PCI express interface supports the PCI conventional bus configuration mechanism
so that the underlying PCI express architecture is compatible with PCI conventional
compliant operating systems.
Ø
PCI
express is a two-way, serial connection that carries data in packets along two
pairs of point-to-point data lanes, compared to the single parallel data bus of
traditional PCI that routes data at a set rate.
PCI
EXPRESS SLOT:
Ø An
expansion slot or expansion bus is a socket on the motherboard where an
expansion card be plugged in.
Ø If
your computer has more expansion slots, you can add more features.
Ø If you purchase a computer, you should ensure that the motherboard has enough expansion cards to suit your future needs
s







.jpeg)










.jpeg)
Post a Comment